What Is the Cost of Manufacturing in Mexico Compared to China?
We analyzed hundreds of news articles and websites to answer the question: Is it cheaper to manufacture in Mexico than in China? We uncovered some interesting findings that may change how you view manufacturing in China compared to Mexico. Please note that the statistics and data presented in this article have been updated to reflect the latest information available. Data has been gathered and analyzed through 2023 and 2024, providing an accurate and current comparison of manufacturing costs in Mexico and China.
Here is a Summary of Our Key Findings:
- Manufacturing Labor Costs are 44% higher in China compared to Mexico.
- Average rent per square foot for industrial space in Mexico is 52% Less expensive than China.
- The Price to Ship a 40-Foot Full Container From China to the United States Is Than 82% Higher Than Shipping From Mexico.
- There Is 514% Increase From 2020 to 2021 in Mexican Suppliers Receiving Bids From Its Big U.S. Buyers and a 155% Increase in Latin American Suppliers Receiving Bids. Manufacturers Sought Goods From 26% Fewer Suppliers in the Asia-Pacific Region.
- In Accordance With the USMCA's Rules of Origin, Goods Are Eligible for Duty-Free Treatment, Avoiding 25% Tariffs. Goods coming from China pay a 25% tariff.
- Europe and Asia are paying up to nearly six times more for natural gas than the U.S. Natural gas prices in Mexico follow those in the U.S.
- The Exchange Rate for the US Dollar In China Is 66% Lower Than the Exchange Rate for the US Dollar in Mexico.
- With $536.7 billion in total (two-way) goods trade, Mexico is a solid, dependable partner.
We have details and additional data from our study below.
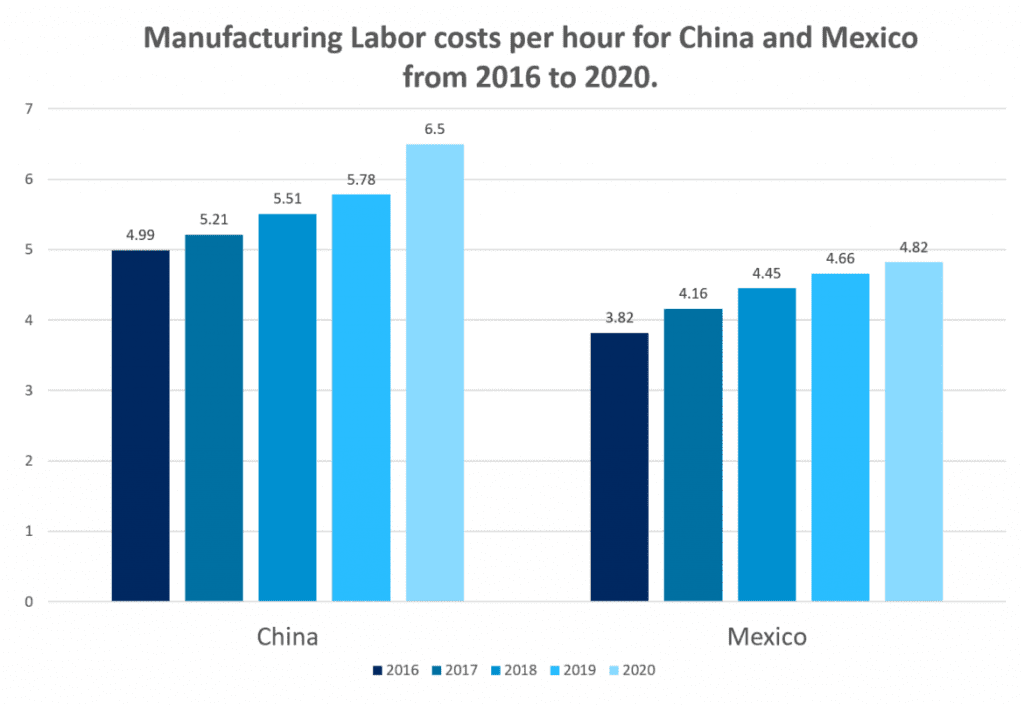
Source: Manufacturing in Mexico vs China, Mexcentrix Strategic Solutions https://topforeignstocks.com/2021/05/24/comparing-manufacturing-labor-cost-in-china-and-mexico/
Manufacturing Labor in Mexico Is Cheaper Than China & Allows for Product Innovation
Several years ago, when China was emerging as a global manufacturing center, labor costs were very low; however, it is not the case anymore as labor costs in China have been steadily increasing for years. Mexico's labor costs make it cheaper to manufacture in Mexico than in China as a result.
A recent study found Mexico's average labor cost per hour to be $4.50, compared to China's $6.50, a 44% difference. Companies in labor-intensive industries can benefit from this cost difference.
In the past decade, China has been shifting from a cheap labor driven economy to more matured, service-oriented markets and industries. While the economy continues to grow, prices and wages keep on increasing as well. - Statista
Companies in Mexico can invest the savings from manufacturing in innovation and features for their customers and products without dealing with high labor costs.
For example, U.S. auto manufacturers are taking advantage of Mexico's low labor costs to include costly fuel-saving features to comply with stricter gas mileage regulations, without increasing car prices.
Wage Stability: Mexico vs. China for Manufacturing Workers
When evaluating wage stability for manufacturing workers, Mexico consistently emerges as a more advantageous option compared to China. Initially, China was lauded for its low labor costs, making it a prime manufacturing destination. However, the wage landscape has shifted over the years.
Comparative Analysis of Wages
According to statistics from the China National Bureau of Statistics and Mexico’s Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI), there is a significant wage disparity between the two nations. As of 2021:
- Average Monthly Wage in China: US $840
- Average Monthly Wage in Mexico: US $480
China's wages have been on a steady upward trajectory, hinting at continued escalation in labor costs. Conversely, Mexico's wages have exhibited remarkable stability, positioning the country as a cost-effective manufacturing hub for the foreseeable future.
Implications for Manufacturing Decisions
The stability in Mexico’s wages can be attributed to various socio-economic factors, thus offering predictability—a crucial element for manufacturers planning long-term investments. Meanwhile, the rising labor costs in China might compel companies to reassess their manufacturing strategies to maintain competitive pricing.
In conclusion, manufacturers seeking wage stability and cost efficiency increasingly find Mexico a more sustainable choice compared to China.
Demographic Trends Affecting Manufacturing Labor in Mexico and China
Shifts in China's Manufacturing Workforce
One significant trend in China is the noticeable decline in its manufacturing labor force. Since hitting a peak in 2011, the number of available workers in this sector has been steadily decreasing. Compounding this issue, China’s overall population has begun to shrink, which directly impacts the long-term sustainability of its labor pool. This decreasing workforce poses challenges for manufacturers looking for a stable and ample source of labor.
Growth in Mexico's Workforce
In contrast, Mexico presents a more positive demographic trend for manufacturing. Mexico's population, currently the tenth largest in the world, continues to grow at an annual rate of 0.8%. This steady population increase ensures a robust influx of new workers to replace those retiring, maintaining a healthy labor pool for the foreseeable future. This demographic stability offers a significant advantage to manufacturers considering relocation or expansion.
Long-term Implications
These trends suggest that while China faces a dwindling labor force, Mexico offers a more sustainable option with its growing population. For manufacturers, this demographic information is crucial for long-term planning and site selection. By opting for Mexico, companies can benefit from a more reliable and expanding labor market.
Warehousing Space is Less Costly in Mexico Than China and There is Plenty Among the US Border
Global supply chains have become increasingly fragile over the past two years. Occupants have responded by realigning their supply chains, leading to a need for more warehouse space closer to their customers.
China's Rent for Warehouse Space
China's average rent for a warehouse space in 2023 was 104.76 yuan ($14.4) per sq ft. The demand for warehouses has been on the rise in that country, leading to rent increases.
Conversely, Statista reports that Mexico City (CDMX) and cities in Mexico
have prices for industrial warehouse rentals per month at $6.87 U.S. per
square meter. This is in Mexico City, Tijuana, and Guadalajara.
Industrial Warehouses in Mexico Continue to Be Characterized by Quality
Industrial warehouses in Mexico will continue to be characterized by quality infrastructure, technological innovations, and strategic locations.
A typical industrial GLA with an average size of 23,000 square meters is scheduled to be developed and delivered in 2024, according to SiiLA.
It appears that large industrial warehouses are being constructed for large-scale logistics and manufacturing operations. There is also a focus on flexible spaces with advanced technologies. These spaces offer
spacious and efficient areas, as well as sustainable and secure features, to meet business needs.
Mexico's industrial sector is evolving, diversifying operations to include advanced logistics, distribution centers, and data centers, among others.
A Boon of Warehousing Along the Texas/Mexico Border
The surge of migrants crossing the US border with Mexico and arriving in cities like New York has grabbed all the headlines—including recent news that migrants in NYC are asking for winter coats and bus tickets to Canada, which is welcoming new immigrants as an expansion of its labor force—but a surge in logistics facilities in towns on the southern border with Mexico is a long-term trend that will have a much larger impact on the US economy.
In fact, it's not a stretch to suggest that both of these trends might intersect in the near-future: with many migrants returning to—or staying near—the Mexican border to help fill the growing number of warehouse jobs that are being created in cities like Laredo, El Paso and San Diego, as well as Tijuana and Tucson, facilities that will need a growing workforce for years to come as labor shortages are expected to persist.
The reshoring of manufacturing and supply chains from Asia—which got a big shout-out from President Biden in his State of the Union Address on Tuesday—is creating a surge in new manufacturing facilities in Mexico, which in turn is fueling development of new and expanded industrial space in border towns. - Globest
“This, in the lingo of corporate executives, is near-shoring, one of the biggest economic transformations sparked by the pandemic: Shrink the length of the supply chain to keep production closer to its final destination and reduce the risk of some snag messing things up along the way. A shorter chain is a stronger chain, the thinking now goes, and there’s a growing sense that this new approach will remain in vogue in C-suites long after Covid fades.
For the multinationals that do business in the red-hot U.S. economy, near-shoring often means northern Mexico, where labor costs are cheap, land is plentiful and the border is just a short ride away. El Paso, Texas, is less than 10 miles to the north of most of the new plants in Juarez.
Other border cities — Tijuana, along the west coast, and Reynosa, Matamoros and Piedras Negras, far to the east — are undergoing similar industrial booms, providing a much-needed lift to a Mexican economy that has been slow to recover from last year’s collapse. “ - Supply Chain Brain
Shipping from China is Expensive and Unreliable
The global supply chain crisis has caused havoc in the shipping community, particularly between Asia and the United States. The cost of containers on these ships is increasing dramatically, not to mention the fierce competition for space on these ships.
According to Dee Freight, a 20 ft. container will cost approximately $6,152 to ship from China to the U.S. West Coast, and a similar container will cost approximately $7,089 to ship to the East Coast of the United States, Additionally, a 40HC container can cost up to $15,000 to ship to the West Coast, and $18,000 to ship to the East Coast.
FreightWays reports that prices for shipping continue to rise and don't appear to be slowing anytime soon.
“The index shows Asia-U.S. West Coast rates at $18,345, six times higher than a year ago, and the price for shipping to the U.S. East Coast quadrupled to $19,620 per forty-foot equivalent unit. Rates from Asia to Northern Europe climbed 4% since last week and are more than eight times higher than a year ago and 2.5 times more than at the start of the year. “
Besides the high rates, there is another issue: due to congestion in many American ports, many ships cannot leave Asian ports, and those that do leave spend many weeks at sea before being delivered.
S&P Global reports that congestion levels at ports in mainland China increased by between 30-40% since March.
Goetz Alebrand, head of Ocean Freight Americas for DHL Global Forwarding, tells CNBC that vessel space on many trade lanes is insufficient to meet market demand. “Trade lanes from Asia to Latin America, Transpacific routes, and Asia to Europe are all experiencing space constraints,” said Alebrand. “These shortages are affecting specific locations, some carriers, and certain types of equipment.”
He cited a shortage of 40-foot containers at the Chinese port of Chongqing last week. “As high demand and longer transit times continue, we are closely monitoring the situation to address any potential challenges,” Alebrand said. - CNBC
Shipping Problems China Is Experiencing Not Affected Goods Coming From Mexico
The shipping problems China is experiencing have so far not affected goods coming from Mexico. The cost of transporting a 40-foot full container load of a shipment worth US $15,000 from Veracruz, Mexico, to San Francisco, California is about US $2,700. The cost of shipping a 40-foot full-truck load with the same value of goods from Mexico to San Francisco is approximately US $1,600.
Mexican manufacturers find rail and trucks to be more cost-effective than waiting for ships at sea to reach congested ports. The US Department of Transportation reports that nearly 35,000 trucks cross the Mexican-US border daily.
Source: Bloomberg. (2022, April).Mexico’s Border Bonanza Shows U.S. Importers Looking Outside China. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/newsletters/2022-04-05/supply-chain-latest-mexico-gains-as-companies-near-shore-from-china
According to Bloomberg, more investment is going to the border regions of Mexico, particularly for shipping:
"Due to strong U.S. demand and a revival of the auto sector, investors are moving in and banks are getting ready to finance new projects. Exports of non-petroleum goods grew almost 27% in February compared with the year earlier. If you’re interested in cars, toys, or medical supplies, there’s probably a company ready to ship through the world’s busiest border."
Rates for shipments crossing the Texas- Mexico border and traveling 501-1,500 miles averaged $2.93 per mile. Time to market is also an added advantage: By ground, goods can be moved from Mexico to the United States in days - and in some cases hours. It is impossible to move shipments that fast when manufacturing products in China.
US Buyers are Buying Manufacturing Materials More in Mexico Than China
Trade tensions between the United States and China have also affected third countries, including Mexico. Since the general
increase in tariffs on Chinese exports, US companies have increasingly looked abroad for raw materials for manufacturing. These raw materials
were previously purchased from China. Mexico's natural status as
an import and manufacturing destination for U.S. businesses has made Mexico a major winner. As global trade patterns have shifted, the United States bought more goods from Mexico than China for the first time in 20 years in 2023.
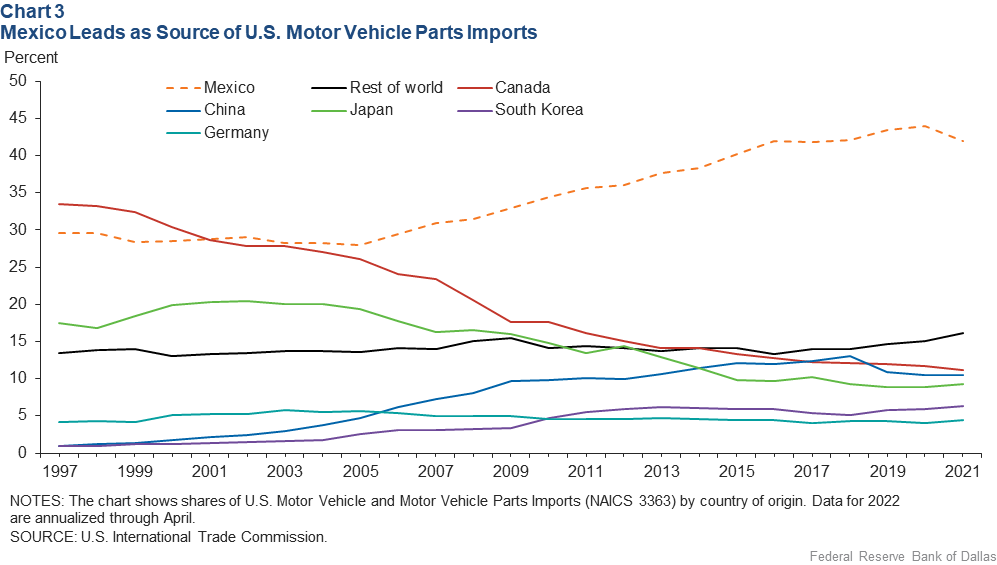
As nearshoring continues and global supply chains are reorganized, Mexico’s manufacturing sector has an opportunity for long-term success, according to Alberto Ramos, head of Latin American economics research at Goldman Sachs, who spoke with CNN.
Ramos said Mexico and China have been competing for the US manufacturing market for years, but amid a shifting US-China relationship, Mexico looks poised to pull ahead.
Mexico surpassed China as the top exporter to the US in 2023. Those exports were driven by manufacturing, which comprises 40% of Mexico’s economy, according to Morgan Stanley. - CNN Business
A country’s competitiveness gives companies insight into what an organization can expect in terms of the institutions, policies, and other factors in place to support business investments. More competitive countries are positioned to attract investments that can create jobs and wealth for their people.
The cost of materials in Mexico is the most important determining factor for manufacturing firms seeking to source materials, although the quality of the goods being sourced is also of critical importance, as is the reliability of getting these materials to their manufacturing plants on time.
Mexico has worked hard to compete in the global market through its numerous free trade agreements and tax incentives. Many local Mexican governments have had extra incentives in place for years to attract manufacturing around certain key industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing. Mexico also competes through investments in educational institutions and training programs that have created a workforce with in-demand manufacturing skills.
China has been, and is still, perceived as the bargain for manufactured products. The economic costs of these massive supply chain disruptions, however, have more than offset these previous bargains. Beyond that, in many cases, the product manufactured in China is no longer always the cheapest. Products with a high labor content are often less expensive when sourced from Mexico. Combine that with shorter lead times, zero duties due to USMCA, competitive transportation costs, reduced cultural differences, and a nation that views itself as an ally and friend of the United States, and Mexico appears to be the clear, strategic choice.”
Shoreview Advisors
The Advantage of Free Trade Agreements Like USMCA Are Clear
Tariffs and Border Taxes on Chinese Goods
Manufacturing in China may initially appear to offer savings, but when you consider the cost of importing these products into the United States, those savings are quickly erased. A set of staged tariff increases were implemented on May 14, 2024, by President Biden on an array of “strategic sectors” imported from China: steel, aluminum, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries, critical minerals, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, and medical supplies.
As of July 2024, imported goods from China are subject to a 35 percent border tax. This tax, along with other tariffs on Chinese products, will increase the cost of buying products from China for American businesses and consumers. Almost all goods are subject to Value Added Tax (VAT), which is typically 13% or 16%. Customs value plus customs duty is used to calculate VAT.
Mexico and Canada Do Not Have Tariffs on Goods Imported Under the USMCA Treaty
As a result of the USMCA treaty, there are no tariffs on goods imported from Mexico and Canada. This makes Mexico cheaper to manufacture than China. It is imperative to know two acronyms if you intend to manufacture in Mexico: USMCA and IMMEX.

Source: National Association of Manufacturers. NAM Releases USMCA State Data Sheets
USMCA
According to Investopedia, USMCA is “…a trade deal between the three nations which was signed on November 30, 2018. The USMCA replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which had been in effect since January of 1994. Under the terms of NAFTA, tariffs on many goods passing between North America’s three major economic powers were gradually phased out.”
There are many reasons why USMCA is significant, but the most important reason is the ability to save money for US businesses. Tariffs have been reduced between the nations; investments have been encouraged in North American industrial buildings, and international markets have been opened. The USMCA provides duty-free treatment for goods that qualify under its rules of origin, which avoid two percent tariffs.
The USMCA has also significantly strengthened U.S. supply chains. COVID-19 and increasing competition with China have highlighted the vulnerability of relying on Chinese supply chains. According to the Brookings Institute:
“The significance of USMCA is clear. Canada and Mexico are the United States’ largest export markets: 23 percent of U.S. exports go to Canada and Mexico (versus 5 percent to China), over 70 percent of Mexican exports are sent to the U.S. and Canada, and 62 percent of Canadian exports are to the U.S. and Mexico. Trade among the countries provides key inputs into regional supply chains’ value added (40 percent U.S. value add versus 5 percent China). “
Labor Cost Savings Provided by IMMEX
Additionally, manufacturers with operations in Mexico should know about IMMEX labor cost savings ("Manufacturing, Maquila, and Export Services Industries Program"; in Spanish, "Maquiladora"). By using the IMMEX program, a manufacturing company can save money on operations that can't be achieved by companies that use manufacturing options in another country, such as China.
The IMMEX program allows manufacturers to reduce their costs by temporarily exporting supplies and equipment to Mexico, having them manufactured or assembled, and re-exporting them to the United States for sale or distribution. Additionally, the IMMEX program provides American manufacturers access to a large, skilled, and economically priced labor pool.
According to the IMMEX program, a manufacturing facility in Mexico that uses temporary imported equipment, tools, and materials is exempt from the entire 16 percent VAT tax.
Energy Costs Are Cheaper in Mexico
Energy costs for powering factories are a major concern for manufacturers all over the world. Global primary energy consumption has increased steadily over the past century due to several factors, including the rapid industrialization of China.
Compared to the rest of the world, China currently has an average industrial power rate of US$0.089/kWh. Compared to China, the average industrial power rate in Mexico ranges from US$0.015/kWh to US$0.21/kWh.
Although the unregulated electricity utilities in Mexico can be higher than those in China, natural gas prices are similar to those in the United States. Compared to the US, China's natural gas costs are between 50 and 170% higher.
China is Dependant on Coal
Chinese commercial primary energy consumption is largely fueled by coal, which accounts for more than 75% of the nation's energy needs. Over half of the world's coal consumption was accounted for by China in 2020, making it the world's largest coal consumer. China's government's emissions-reduction campaign, however, is causing energy shortages in many of the country's main manufacturing provinces due to plunging coal supplies caused by the campaign.
Justin Floyd, CEO of ecommerce and distribution company RedCloud, discusses the impact of the coal shortage on Chinese manufacturing production.
“If you’ve got no energy, your factories are on kind of a complete standstill, and when your factories are on standstill, you’re not producing any goods; what we’re seeing is the global impact it has by highlighting how many countries have been and are reliant on China.”
Mexico and Renewable Energy
Mexico is investing in renewable energy sources that may reduce
its electricity costs by the end of the decade. This is unlike the Chinese who look
for alternative energy sources in the opposite direction. With Claudia Sheinbaum as Mexico's elected prime minister in 2024, and Sheinbaum being an expert in climate science, the green energy programs are likely to continue and accelerate.
The Government of Mexico’s (GoM) energy transition law sets the target for 35% of its electricity generation to come from clean energy sources by 2024. Mexico is well on its way to meeting this aim, generating 26.7% of its electricity from renewable sources in 2021. However, it will have to continue to expand its renewable sector as electricity demand in Mexico is expected to grow by 12.7% by 2024. - Mexico Energy LLC
Source: McKinsey& Company. (2019, November).How Mexico can harness its superior energy abundance. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/oil-and-gas/our-insights/how-mexico-can-harness-its-superior-energy-abundance
The Exchange Rate for the US Dollar is Better in Mexico Than China
The Yuan exchange rate is a cornerstone of China's economic policy. Most advanced economies have floating exchange rates determined by market forces, but not China. Rather, the yuan (or renminbi) is pegged to the dollar. This practice allows the Chinese to keep their exchange rate at a favorable level regardless of market performance. As a result, your dollar investment will not get very far if it is invested in China.
Furthermore, the true exchange rate of dollars to Yuan is difficult to determine because the Chinese government consistently undervalues its currency. According to Investopedia:
“The true value of the yuan is difficult to ascertain, and although various studies over the years suggest a wide range of undervaluation - from as low as 3% to as high as 50% - the general agreement is that the currency is substantially undervalued. By keeping the yuan at artificially low levels, China makes its exports more competitive in the global marketplace.”
Mexico Exchange Rate is Lower
Mexico, on the other hand, has a 66% lower exchange rate for the US Dollar than with China. Years of conservative fiscal policies have paid dividends for the Mexican peso allowing it to become one of the strongest worldwide market currencies. The Mexican peso is uniformly low against the dollar throughout the country, so your money will go far wherever you are.
A recent analysis by Ramsé Gutiérrez, senior vice president and co-director of investments at Franklin Templeton Mexico, indicated that the rate hit a high in early March following Russia's invasion of Ukraine, reaching 21.4 pesos to a dollar. It has since appreciated steadily, reaching 19.5 to a dollar.
The proximity of Mexico to the U.S. and our shared border also contributes to the Peso's liquidity. Investopedia
“Physical proximity has an additional effect on the peso’s value. Highly prosperous border regions engaging in commercial interactions significantly increase Mexican peso liquidity.”
Investopedia
China Cannot Compete With Mexico's Shelter Manufacturing as a New Destination
In the face of trade tariffs against China and the Chinese government's zero-Covid policies, manufacturing companies in the US and other international locations are rethinking China and their operations in Asia as a whole. Mexico is considered the best location. Mexico offers manufacturing destinations advantages China cannot match.
Mexico to Gain a Competitive Advantage Over China in US Manufacturing
As the US-China relationship shifts, Mexico looks poised to gain a competitive advantage over China in the US manufacturing market.
In 2023, Mexico became the top exporter to the United States. According to Morgan Stanley, Mexico's exports were driven by manufacturing, which accounts for 40% of its economy.
According to Commerce Department data released on April 4, US imports from Mexico increased in February. Compared to 2022, Chinese exports to the US were down 20% in 2023.
“Mexican business leadership is still very optimistic about Mexico’s future. They understand Mexico’s treaty obligations in the USMCA and the opportunities it presents for Mexico. They wring their hands about AMLO’s (President Andrés Manuel López Obrador) trajectory, but they are determined to succeed by continuing to build the business environment with or without the government’s help.
China Law Blog
“Mexico is not the only country that will benefit from China’s current negative trajectory, but if Mexico’s government is paying attention, it will have more fuel to root out the less desirable hurdles to doing business in Mexico. For companies leaving China for Mexico, this cannot happen soon enough.”
Moving Manufacturing to Mexico Can Save Time and Paperwork
Additionally, moving manufacturing to Mexico can save time and paperwork, which will ultimately result in significant cost savings. For these reasons, U.S. goods and services trade with Mexico totaled an estimated $577.3 billion in 2021.
Reduction in Legal Liability
A foreign investor doing business in Mexico through a Mexican subsidiary has traditionally been protected from liability for the debts and obligations of the Mexican subsidiary.
Knowledge of Mexico Business Practices
Manufacturing companies often make the mistake of assuming they know enough about Mexico to do it on their own. The majority of shelter manufacturers can assist you in cutting through the red tape in starting your manufacturing operation by providing analyses, site visits, classifications, permits, factory setup, and training. Also, Mexico's industrial capabilities make choosing a location for a manufacturing operation less difficult; most places in the country have some sort of industrial facility, although some locations are more suitable than others.
Proximity to the U.S.
One of the most compelling reasons for choosing Mexico over China for manufacturing is its proximity to the U.S. This geographical advantage reduces shipping times, making logistics simpler and faster. Executives can travel between the two countries more easily and at a lower cost, facilitating hands-on management, routine training, logistical oversight, and quality control checks.
Shared Time Zones and Communication
Sharing time zones significantly simplifies real-time communication, enhancing coordination and reducing delays. This boosts manufacturing efficiency and allows for seamless interaction between U.S. And Mexico-based teams.
Unique Advantages of Different Locations
Different sites within Mexico offer unique advantages. Evaluating various locations within the country can reveal specific benefits tailored to your business needs. From proximity to major transportation routes to local workforce expertise, each region has its own strengths.
Cultural and Language Similarities
Cultural and linguistic similarities streamline management processes and open communication channels, making operations smoother and more efficient. This is an often-overlooked but critical factor in operational simplicity.
Quick Setup Model
There are many factors that influence this, such as equipment, training and sourcing materials. However, some companies who are interested in starting manufacturing in Mexico can do so within a month. Since many shelter manufacturing companies are incorporated in Mexico, and hold current maquiladora permits, there is no legal aspect to this process.
Protection of Intellectual Property
Intellectual property theft is a tremendous problem in China. The new USMCA agreement strengthens intellectual property rights even further in Mexico, with one of its main objectives to protect the Intellectual Property Rights of products between the United States, Mexico, and Canada. In accordance with the Office of the United States Trade Representative:
“The United States, Mexico, and Canada have reached an agreement on a modernized, high-standard Intellectual Property (IP) chapter that provides strong and effective protection and enforcement of IP rights critical to driving innovation, creating economic growth, and supporting American jobs.”
By enforcing these rights, it becomes very difficult, if not impossible, for companies manufacturing in Mexico to have their intellectual property rights stolen.
Conclusion: It is Cheaper to Manufacture in Mexico Than in China
In conclusion, Mexico's strategic initiatives and investments in education, combined with competitive costs and logistical advantages, position it as a formidable competitor to China in the global manufacturing landscape. As companies seek reliable and economically viable alternatives, Mexico's growing export numbers and business-friendly environment make it an attractive choice.
- Manufacturing Labor is Less Expensive and More Plentiful than in China
- There is an abundance of warehousing and manufacturing space on the border of the US & Mexico (particularly in Texas) that is significantly cheaper than in China.
- In light of the current supply chain problems using sea freight, the speed of goods arriving from Mexico to the US is perhaps the greatest advantage offered by manufacturing in Mexico. Compared to China, it takes a fraction of the time to reach American warehouses and stores.
- US buyers, citing poor quality and delays from China, are buying more goods and supplies from Mexico factories.
- Due to the US Free Trade Agreement with Mexico, it is relatively inexpensive and almost seamless to move goods across the border. Currently, Chinese goods entering the US are subject to high tariffs, which makes transporting them to American markets very expensive.
- Mexico's energy costs are comparable to those in the United States, making them both cheaper and more environmentally friendly. China has a high dependence on coal, and there is a gas shortage, making energy costs high and causing frequent power outages.
- The exchange rate for the peso compared to the US dollar is very favorable, allowing investments in Mexico to extend further than investments in China.
- The intangibles of manufacturing in Mexico; easy setup model, protection against intellectual property theft and limited legal liabilities are benefits not offered in China.
About NovaLink
As a manufacturer in Mexico, NovaLink employs a unique approach that transcends the traditional model of shelter production. More than just the location of your manufacturing, we would like to become a partner in your manufacturing in Mexico. You will be able to relocate or initiate manufacturing for your company in Mexico in a low-cost labor environment with very little delay or up-front costs. Find out how we can help you by handling the manufacturing process.
There are NovaLink facilities in the border cities of Brownsville, Texas, Matamoros, Mexico, and Saltillo, Mexico.