Last Updated on June 12, 2024
Mexico is one of the leading players in the global manufacturing landscape. In recent years, the manufacturing industry in the country has undergone a remarkable transformation and growth. In this article, we will explore how Mexico's manufacturing sector compares to other countries, highlighting its strengths, challenges, and future prospects.
The Rise of Mexico's Manufacturing Industry
Mexico's manufacturing industry has grown dramatically over the past few decades. The country's strategic location, favorable trade agreements, and competitive labor costs have attracted numerous multinational corporations. From automotive and electronics to aerospace and medical devices, Mexico has become a preferred manufacturing hub for various sectors.
In the third quarter of 2022, the Mexican economy grew 4.3% year over year (YoY), a number that doubled expectations at a time when the world economy is decelerating. This uptick in growth saw the GDP reaching 18.4 billion pesos (920 billion US dollars), the same level registered in the fourth quarter of 2019, prior to the onset of the pandemic. Therefore, this expansion, eleven quarters after the pandemic, marks an important milestone in Mexico’s post-pandemic recovery process. The uptick was mainly driven by robust growth in manufacturing activities and private consumption throughout 2022.
Deloitte, Mexico economic outlook, December 2022
Key Factors Contributing to Mexico's Success
Strategic Location: Mexico's proximity to the United States, one of the world's largest consumer markets, has changed the manufacturing industry. Geographic advantages facilitate goods movement, reducing transportation costs and lead times.
Free Trade Agreements: Mexico has entered into numerous free trade agreements, such as NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) and USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement), which have significantly boosted cross-border trade and investment.
Competitive Labor Costs: Compared to many developed countries, Mexico offers lower labor costs without compromising work quality. This has made it an attractive destination for labor-intensive manufacturing processes.
Comparison with Other Countries
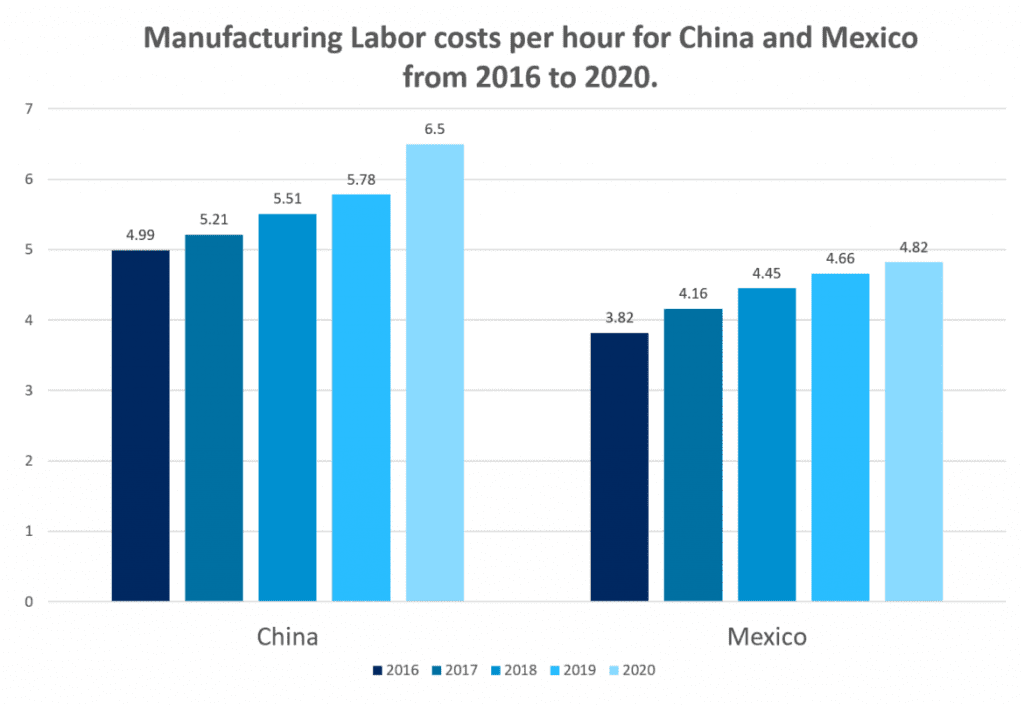
Mexico vs. China
Mexico and China are often compared as manufacturing powerhouses. While China leads in terms of the sheer scale of production, Mexico offers certain advantages:
Proximity to the U.S. Market: Mexico's proximity reduces shipping times and transportation costs compared to China, making it an attractive option for companies supplying the US.

The index shows Asia-U.S. West Coast rates at $18,345, six times higher than a year ago, and the price for shipping to the U.S. East Coast quadrupled to $19,620 per forty-foot equivalent unit. Rates from Asia to Northern Europe climbed 4% since last week and are more than eight times higher than a year ago and 2.5 times more than at the start of the year.
FreightWaves
Lower Import Tariffs: With the implementation of the USMCA, Mexican goods can benefit from lower import tariffs than Chinese products, providing a competitive edge.
Ease of Doing Business: Mexico's business-friendly environment and cultural affinity with the West make it easier for companies from Europe and North America to establish operations.
Mexico vs. Vietnam
Vietnam has emerged as a formidable competitor in manufacturing, especially in apparel and electronics. When compared to Vietnam, Mexico offers:
Quality and Diversification: Mexico is known for producing high-quality goods and has a more diversified manufacturing base than Vietnam.
Closer Market Access: Similar to its advantage over China, Mexico's proximity to the US provides better access to the North American market.
Infrastructure: Mexico's well-developed infrastructure is often considered superior to Vietnam's, which facilitates smooth logistics and supply chain operations.
Vietnam only has 4 major ports: Hai Phong, Da Nang, Qui Nhon, and Ho Chi Minh City. Vietnam ranks 80 among 139 countries on the quality of port infrastructure, with an average score of 3.80 on a scale of 1 (lowest) to 7 (highest) between 2006 and 2018. This means Vietnam ranks lower than countries such as China, India, Thailand, and Sri Lanka. According to Vietnam briefing:
Vietnam Briefing
“Vietnam has 44 seaports with a total capacity of 470-500 million tons per year. The Vietnam Port Association (VPA) states that 80 percent of container exports and imports go through smaller ports and ships, a process known as transshipment. The VPA also noted that goods owners have losses of approximately US$2.4 billion each year due not using deep-water ports.”
Future Prospects for Mexico's Manufacturing Industry
The future looks promising for Mexico's manufacturing industry. Despite some challenges, the country continues to attract foreign investments and expand its industrial base. To ensure sustained growth, the government is focusing on:
Investing in Education: The government is channeling resources into improving the education system to create a more skilled workforce, thus meeting industry's demands.
Enhancing Research and Development: Emphasizing innovation and R&D will enable Mexico to move up the value chain and produce cutting-edge products.
Diversifying Export Markets: While the US remains a significant market, Mexico is exploring opportunities in other regions to reduce its dependency and diversify its export destinations.
Conclusion
Mexico's manufacturing industry has come a long way, emerging as a vital player on the global stage. Its strategic advantages, competitive labor costs, and proximity to major markets have fueled its growth. While challenges persist, Mexico's commitment to investment, innovation, and diversification points towards a promising future for its manufacturing sector.
FAQs on Mexico's Manufacturing Industry
Q1: Is Mexico's manufacturing sector still growing?
A1: Yes, Mexico's manufacturing sector continues to grow steadily, attracting foreign investments and expanding its industrial base.
Q2: What industries are prominent in Mexico's manufacturing sector?
A2: Mexico's manufacturing sector encompasses industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and more.
Q3: How does Mexico compare to China in terms of manufacturing costs?
A3: While China still offers lower labor costs, Mexico's proximity to the US and lower import tariffs under USMCA make it competitive in manufacturing costs.
Q4: How is the Mexican government addressing the skilled workforce gap?
A4: The Mexican government is investing in education and training programs to bridge the skilled workforce gap in the manufacturing sector.
Q5: What are the main challenges faced by Mexico's manufacturing industry?
A5: Some of the main challenges include dependence on the US market, security concerns, and a shortage of skilled workers in certain areas.
About NovaLink
As a manufacturer in Mexico, NovaLink employs a unique approach that transcends the traditional model of shelter production. More than just the location of your manufacturing, we would like to become a partner in your manufacturing in Mexico. You will be able to relocate or initiate manufacturing for your company in Mexico in a low-cost labor environment with very little delay or up-front costs. Find out how we can help you by handling the manufacturing process.
There are NovaLink facilities in the border cities of Brownsville, Texas, Matamoros, Mexico, and Saltillo, Mexico.