Last Updated on June 3, 2025
When it comes to the world of manufacturing, Mexico has emerged as a significant player in manufacturing. With a diverse array of industries and a commitment to innovation, Mexico's manufacturing processes have evolved and adapted to meet the demands of the modern market. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of manufacturing processes in Mexico. We will explore the methods, technologies, and trends that drive this dynamic sector.
The Manufacturing Landscape in Mexico
Mexico's manufacturing sector is a cornerstone of its economy, contributing substantially to GDP. Over the years, Mexico has evolved from traditional manufacturing to embrace a broad range of industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and more.
The Economic Impact of Mexico’s Automotive Industry
The automotive sector stands as a driving force within Mexico’s manufacturing landscape, shaping both economic output and employment. In recent years, this industry has not only established itself as a global powerhouse—now ranking as the world’s sixth-largest producer of passenger vehicles—but also cemented its position domestically. Automotive manufacturing contributes a substantial portion to Mexico’s GDP, accounting for just over one-fifth of the nation’s total economic activity. This makes it second only to the food industry in terms of sheer economic significance.
On an annual basis, Mexican plants assemble close to 5 million vehicles, with the vast majority destined for export markets, particularly the United States. This robust export activity generates impressive revenues, with annual figures soon expected to exceed $100 billion. Such vibrant growth is mirrored in employment: the sector provides jobs for over a million Mexicans, driving local communities and reinforcing the country’s reputation as a vital link in the global automotive supply chain.
Modernization and Expansion of Mexican Textile Manufacturers
Mexican textile manufacturers have been making significant strides in modernizing their operations. Many have invested in updated facilities and new technologies, allowing them to move beyond traditional textile products.
This modernization is enabling a shift into new markets, particularly automotive and industrial fabrics. For example, upgraded textile plants in Puebla are now producing components like filters, airbags, seat covers, doors, and bands for major automotive companies including Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW.
These advancements not only strengthen Mexico’s position in automotive manufacturing but also highlight the adaptability and diversification of its textile sector in meeting the needs of global industries.
Nearshoring has the potential to boost the growth of Mexican manufacturing exports to the U.S., from $455 billion today to an estimated $609 billion in the next five years. Manufacturing exports currently represent about 40% of Mexico's $1.3 trillion economy.
Morgan Stanley
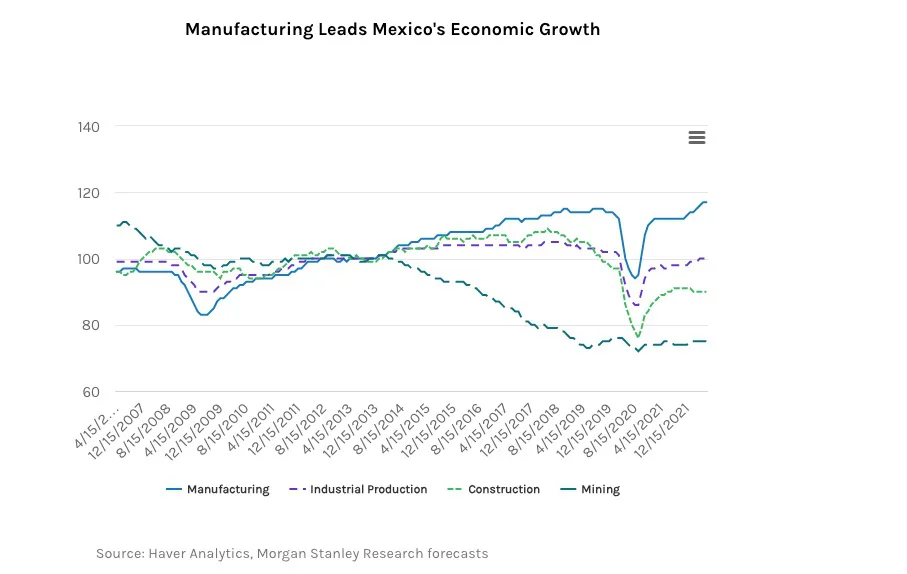
Trends in Foreign Investment and Job Creation in Mexico’s Aerospace Sector
Mexico’s aerospace industry stands out as a testament to the country’s industrial transformation and international appeal. Over the past decade, the sector has experienced a remarkable influx of foreign investment, which has played a pivotal role in fueling both growth and innovation.
Consider some telling figures: direct foreign investment in the aerospace industry soared past $6 billion between 2007 and 2017. During that same stretch, the number of aerospace firms operating in Mexico nearly tripled, rising from just over a hundred to more than 300. This expansion isn’t just about numbers on a balance sheet—it translates to significant job creation. For example, between 2013 and 2016 alone, tens of thousands of new jobs were generated, reflecting average annual export growth rates of 20% according to data from trade.gov.
Driving these gains are a mix of forward-looking government initiatives—think new workforce training programs, targeted business incentives, and expansion of universities designed to cultivate technical expertise. This collaborative push has made the aerospace sector one of the top performers in Mexico, positioning it to benefit from rising global demand for both new aircraft and maintenance services in a post-pandemic world.
In short, Mexico’s aerospace sector exemplifies how strategic foreign investment, paired with robust government support, can spark widespread employment opportunities and sustained industrial advancement.
Mexico’s Apparel and Textile Industry: Economic Impact
While industries like automotive and electronics often dominate the headlines, Mexico’s apparel and textile manufacturing remains a vital thread in the fabric of the nation’s economy. As the fourth-largest manufacturing sector, textiles and apparel collectively contribute a notable share to the country's manufacturing GDP—helping to diversify economic activity beyond just vehicles and gadgets.
Several factors fuel the industry’s steady growth. For starters, ongoing modernization efforts have transformed textile manufacturing facilities, enabling them to serve not just fashion and clothing demands but also the evolving needs of sectors like automotive and industrial components. This adaptability is particularly evident in regions such as Puebla, where factories now supply specialized products like filters, airbags, and seat covers to global automotive giants.
Such advancements do more than expand output—they generate skilled jobs, stimulate local supply chains, and attract foreign investment. In turn, this sustained momentum fortifies Mexico’s position as a key player in North America’s integrated manufacturing ecosystem.
Types of Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing in Mexico encompasses various processes, each tailored to different industries.
Traditional vs. Modern Manufacturing Methods
Traditional manufacturing techniques and advanced, technology-driven methods represent two distinct approaches to producing goods. These approaches differ significantly in terms of processes, capabilities, and outcomes. Here's an overview of the key distinctions between the two:
Traditional Manufacturing Techniques:
- Labor-Intensive: Traditional manufacturing methods rely heavily on manual labor and skilled craftsmen. Workers perform tasks such as cutting, shaping, and assembling components by hand.
- Low Automation: Automation is minimal in traditional manufacturing. Machines are often simple and require human operators to control and adjust them.
- High Variability: There can be a high degree of variability in the final product due to manual processes. Quality control is often performed through visual inspection.
- Limited Precision: Traditional techniques may limit high precision and tolerances. Complex or intricate designs can be challenging to produce consistently.
- Slower Production: Traditional manufacturing is slower than technology-driven methods. It may take longer to fulfill orders and adapt to changing demands.
- Skill-Dependent: Traditional methods rely on craftsmen's skills and experience, which can lead to challenges scaling production or maintaining consistent quality.
- Higher Labor Costs: Labor costs are a significant component of traditional manufacturing, particularly in regions with higher wage rates.
Advanced, Technology-Driven Methods:
- Automation and Robotics: Technology-driven manufacturing heavily relies on automation, robotics, and computer-controlled machinery. These systems can perform repetitive tasks with high precision and speed.
- Digitalization: Advanced methods often incorporate digital technologies such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD), Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM), and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) for seamless integration and data-driven decision-making.
- Consistency and Quality: Technology-driven methods offer higher consistency and quality control. Sensors and monitoring systems ensure products meet precise specifications.
- Flexibility: Advanced methods are more adaptable to changes in production volume and product design. Rapid retooling and reprogramming of machines is possible.
- Higher Precision: Technology-driven processes can achieve extremely high precision and tight tolerances, making them suitable for complex and critical applications.
- Speed and Efficiency: Automation and technology-driven methods significantly increase production speed and efficiency, reducing lead times and production costs.
- Lower Labor Costs: While initial investments in technology can be substantial, ongoing labor costs tend to be lower as automation reduces the need for a large workforce.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Technology-driven manufacturing relies on data analytics to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency continuously.
Automation Revolutionizing Manufacturing in Mexico
Automation and robotics have revolutionized manufacturing processes in Mexico, bringing numerous advantages to the industry.
Adoption of Automation and Robotics
Mexican manufacturers are increasingly adopting automation and robotics in their production processes to enhance efficiency, precision, and competitiveness. This shift toward automation is driven by several factors, including cost savings, improved product quality, and the need to remain competitive on the global market.
Mexico is among the five largest importers of advanced manufacturing technology globally. This sector has grown exponentially since 2020 as companies have started nearshoring to Mexico. Through their adoption of AM tools, Mexican manufacturers are investing in the technological advances needed to remain and stay ahead of the competition.
International Trade Administration
Here's an exploration of how Mexican manufacturers integrate automation and robotics into their operations:
- Automotive Industry: Mexico has a significant presence in the automotive sector, and automation plays a pivotal role. Automotive manufacturers in Mexico have adopted robotic arms for welding, painting, and assembly. These robots ensure consistent quality, reduce defects, and enhance production rates.
Mexico’s automotive industry is central to the nation’s economy, attracting global giants like Fiat Chrysler, Ford, GM, and Toyota. As South America’s largest automotive manufacturer, Mexico produces close to 4 million units annually—with approximately 82% destined for export. This industry represents more than 20% of the country’s GDP, second only to the food industry, and employs over a million people nationwide.
Automation and robotics are integral to meeting the high standards required by international partners and regulatory frameworks. For example, advanced manufacturing technology enables Mexican plants to comply with USMCA requirements, which mandate that 75% of a vehicle’s content originate in North America and that core parts be sourced from Mexico, the U.S., or Canada. These regulations are shaping the industry, driving further investment in automation, and opening new opportunities for both local suppliers and exporters.
By leveraging cutting-edge automation, Mexico’s automotive sector has become the sixth-largest passenger vehicle producer in the world, manufacturing nearly 5 million vehicles each year—a number that continues to grow. This commitment to innovation ensures that manufacturers not only maintain global competitiveness but also deliver quality vehicles at scale. - Aerospace Industry: Mexican manufacturers use automation and robotics for precision machining, composite manufacturing, and quality control. These technologies enable the production of complex components with the tight tolerances required for aerospace applications.
- Government Initiatives Fueling Aerospace Growth: The rapid growth of aerospace manufacturing in Mexico owes much to a range of targeted government programs designed to support the industry’s expansion and global competitiveness. One of the key pillars has been the IMMEX Program—originally launched as the Maquiladora Export Program in the late 1960s—which allows manufacturers to temporarily import raw materials and parts without incurring import duties or taxes, provided the finished goods are exported. This strategy has been especially attractive for aerospace companies seeking cost-effective, streamlined operations.
In addition, the government has invested heavily in workforce development to meet the sector’s specialized needs. This includes the establishment of workforce training programs and the founding of new technical universities geared toward advanced manufacturing, engineering, and aerospace skills. These initiatives not only help build a skilled labor pool but also support ongoing innovation within the industry.
Furthermore, government incentives such as tax breaks and grants have encouraged both domestic and international investment. Combined with steadily increasing global demand for new aircraft and maintenance services, these supportive measures position Mexico as a thriving hub for aerospace manufacturing. - The aerospace sector in Mexico has seen remarkable growth, driven in part by proactive government initiatives like the Maquiladora Export Program (now known as the IMMEX Program). This program laid a strong foundation for industrial expansion by allowing goods to be imported, assembled, and exported without import duties or taxes—making Mexico an attractive destination for aerospace manufacturing.
- Over the past decade, the industry has achieved impressive milestones:
- From 2013 to 2015, aerospace exports grew at an average annual rate of 20%.
- By 2016, the sector had generated around 63,000 jobs.
- Direct foreign investment between 2007 and 2017 exceeded $6 billion.
- The number of aerospace firms operating in Mexico jumped from 112 in 2009 to over 330 by 2017.
- To support this rapid expansion, the Mexican government launched various employment programs, business incentives, workforce training initiatives, and new universities focused on technical education. As global demand for new aircraft and maintenance services rises—especially in the wake of COVID-19—Mexico’s aerospace industry is poised for continued growth, fueled by automation, robotics, and a skilled workforce.
- Government Initiatives Fueling Aerospace Growth: The rapid growth of aerospace manufacturing in Mexico owes much to a range of targeted government programs designed to support the industry’s expansion and global competitiveness. One of the key pillars has been the IMMEX Program—originally launched as the Maquiladora Export Program in the late 1960s—which allows manufacturers to temporarily import raw materials and parts without incurring import duties or taxes, provided the finished goods are exported. This strategy has been especially attractive for aerospace companies seeking cost-effective, streamlined operations.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Mexico is a hub for electronics manufacturing, and automation is crucial for producing consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment. Robotic assembly lines and automated testing stations ensure speed, accuracy, and quality control.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Even in the food and beverage sector, automation is gaining traction. Mexican food manufacturers use robotic systems for packaging, labeling, and palletizing. This improves efficiency and food safety and hygiene.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Precision and quality are paramount in medical device manufacturing. Robotic assembly, inspection, and packaging systems help Mexican manufacturers meet stringent regulatory requirements while increasing production output.
Mexico’s medical device sector has seen robust growth over the past decade, with hundreds of companies—many clustered along the U.S./Mexico border—leveraging nearshore operations to take advantage of proximity to the U.S. market. This region alone supports a substantial workforce and contributes billions in annual exports. Several factors fuel the industry’s expansion:- A highly-trained and educated workforce, ensuring adherence to global standards
- Strong collaboration among academic institutions, government agencies, and the private sector to drive innovation, efficiency, and compliance
- The logistical and cost advantages provided by Mexico’s location, making it a competitive alternative to other manufacturing hubs like China
- As a result, automation and robotics have become central to the success of medical device manufacturing in Mexico, enabling companies to efficiently scale production, maintain rigorous quality control, and meet the exacting demands of international markets.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Collaborative robots, or cobots, find applications in Mexican manufacturing. These robots work alongside human operators, assisting with tasks like material handling, assembly, and quality inspection. Cobots are often used in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that have limited floor space or resources for large-scale automation.
- Cost Savings: Mexican manufacturers are drawn to automation and robotics because they offer long-term cost savings. Although the initial investment can be significant, reduced labor costs, improved efficiency, and decreased defect rates contribute to a quick return on investment (ROI).
- Training and Skill Development: As automation becomes more prevalent, Mexican manufacturers are investing in training and upskilling their workforce to operate and maintain robotic systems. This investment in human capital ensures a seamless transition to automated processes.
A highly trained and educated workforce is a major driver behind the success of automation in Mexico’s manufacturing sectors, particularly in regions near the U.S. Border. Here, the medical device industry has seen remarkable growth, with hundreds of companies providing significant employment opportunities and contributing billions of dollars to exports annually.
Academic, government, and private sector collaborations further expand the capabilities of device manufacturing and enhance operational efficiency. With Mexico’s proximity to the U.S., manufacturers also benefit from cost-effective logistics and faster delivery times compared to overseas competitors.
The ongoing focus on workforce development, strong industry partnerships, and geographic advantages position Mexico as a global leader in advanced manufacturing. - Integration of Industry 4.0: Mexican manufacturers are also embracing Industry 4.0 principles by incorporating sensors, data analytics, and connectivity into their automated systems. This enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
- Global Competitiveness: Automation and robotics help Mexican manufacturers remain competitive globally. By improving production efficiency and product quality, they can meet international markets' demands and attract foreign investment.
Lean Manufacturing Principles
Explanation of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a production philosophy and methodology that focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency in manufacturing processes. It originated from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and has since been widely adopted by manufacturing companies around the world. Lean manufacturing aims to enhance production by streamlining operations, reducing costs, improving quality, and increasing overall productivity.
Lean Practices in Mexican Manufacturing
Mexican manufacturers have increasingly adopted lean principles to optimize their operations and improve competitiveness in global markets. By implementing lean methodologies, they aim to eliminate waste, enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality products. Here's how Mexican manufacturers implement lean principles:
- Cultural Transformation: Implementing lean begins with cultural transformation within the organization. Mexican manufacturers focus on building a continuous improvement culture, involving all employees in identifying and solving problems. This cultural shift encourages engagement and empowers employees to contribute to process optimization.
- Value Stream Mapping: Value stream mapping is a crucial tool in lean manufacturing. Mexican manufacturers use it to analyze production processes and identify waste areas. This visual representation helps them understand the flow of materials and information and highlights opportunities for improvement.
- 5S Methodology: Mexican manufacturers implement the 5S methodology (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) to organize the workplace for efficiency and safety. This approach improves workspace organization, cleanliness, and visual management, which are fundamental aspects of lean.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: JIT is a key component of lean manufacturing. Mexican manufacturers aim to produce goods only when needed to minimize excess inventory and reduce carrying costs. JIT principles also help respond quickly to customer demand changes.
- Kanban Systems: Kanban systems signal the need for replenishing materials or parts. Mexican manufacturers employ Kanban cards or electronic systems to control materials flow, ensuring production remains synchronized with demand.
- Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Kaizen is an integral part of the lean culture in Mexican manufacturing. It involves regular, incremental process improvements, often led by cross-functional teams. These small, ongoing changes add up to significant improvements over time.
- Cross-functional Teams: Mexican manufacturers establish cross-functional teams with employees from various departments to work on process improvement projects. These teams collaborate to solve problems, share expertise, and drive innovation.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM): TPM aims to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Mexican manufacturers implement TPM practices to ensure machinery is well-maintained and operates optimally.
- Quality Control: Lean principles emphasize building quality into the production process from the start rather than inspecting for defects afterwards. Mexican manufacturers focus on reducing defects and improving first-pass quality to save time and resources.
- Supplier Involvement: Lean extends beyond the factory floor to involve suppliers. Mexican manufacturers collaborate with their suppliers to optimize supply chains, reduce lead times, and ensure timely materials delivery.
- Training and Skill Development: Mexican manufacturers invest in employee training. They ensure that their workforce is well-equipped to understand and implement lean principles effectively.
- Digital Technologies: Many Mexican manufacturers leverage digital technologies, such as Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions, to collect and analyze data for continuous improvement and real-time monitoring.
- Benchmarking and Best Practices: Mexican manufacturers benchmark their performance against industry best practices and global competitors. This helps identify areas for improvement and sets performance targets.
Custom Manufacturing and Outsourcing
Custom manufacturing and outsourcing have become prevalent in Mexico due to their advantages.
Advantages of Custom Manufacturing
Custom manufacturing is gaining popularity due to the growing demand for personalized and unique products across various industries. This approach allows manufacturers to cater to the specific needs and preferences of individual clients, offering benefits such as flexibility, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Here's why custom manufacturing is on the rise and how it caters to unique client needs:
- Diverse Customer Demands: Customers today have diverse and evolving preferences. They seek products tailored to their individual tastes, whether in fashion, electronics, furniture, or other industries. Custom manufacturing allows companies to meet these demands effectively.
- Market Segmentation: Businesses increasingly recognize the value of market segmentation. Custom manufacturing enables companies to target niche markets and cater to unique requirements, enhancing market share and competitiveness.
- Product Differentiation: Customization is a powerful tool for product differentiation. It allows manufacturers to create distinct offerings in a crowded marketplace, setting them apart from competitors and attracting discerning customers.
- Personalization: Personalized products create a stronger emotional connection between consumers and brands. Whether it's monogrammed apparel, customized jewelry, or personalized tech gadgets, clients appreciate products that reflect their identity or preferences.
- Quality Control: Custom manufacturers often have more control over the production process, leading to higher quality products. Each item can be crafted with precision and attention to detail, reducing defects or errors.
- Innovation: Custom manufacturing drives innovation. Manufacturers constantly develop original and creative solutions to meet individual client needs, leading to advancements in product design and functionality.
- Customer Satisfaction: Tailoring products to customer specifications enhances overall satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal, repeat buyers and advocates for the brand.
- Rapid Prototyping: Advances in technology, such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD), have made it easier and more cost-effective to create prototypes and test custom designs before full-scale production. This accelerates product development.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Custom manufacturing can lead to a more efficient supply chain. By producing products as ordered, manufacturers can reduce inventory, storage costs, and waste.
- Sustainability: Custom manufacturing can align with sustainability goals. It allows only what is needed, minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact.
- Business Model Flexibility: Custom manufacturing provides flexibility in business models. Companies can offer standard products alongside custom options, catering to a broad range of customers.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that excel at custom manufacturing can gain a significant competitive advantage. Customers are willing to pay a premium for products that meet their specific needs, which translates into higher margins.
- E-commerce Growth: E-commerce growth has made it easier for customers to access and order custom products online. Online platforms and configurators make it easy to design and purchase customized items.
Mexico as a Manufacturing Outsourcing Destination
Mexico has emerged as a prominent outsourcing hub, offering cost-effective and specialized production services to businesses around the world. Its strategic location, skilled workforce, and competitive advantages make it an attractive destination for companies seeking to outsource various manufacturing and service-related activities. Here's an overview of Mexico's role as an outsourcing hub and its benefits to businesses:
- Proximity to Major Markets: Mexico's geographical proximity to the United States and Canada makes it an ideal choice for companies looking to serve North American markets. Shorter shipping distances reduce transportation costs and lead times, enhancing supply chain efficiency.
- Skilled Workforce: Mexico boasts a well-educated and skilled workforce, particularly in manufacturing and technology-related fields. The availability of a large labor pool with technical expertise allows businesses to find talent for specialized tasks. In recent years, Mexico’s labor pool has not only grown in size but also in sophistication, supporting diverse and advanced manufacturing activities.
- Competitive Labor Costs: Mexico's labor costs are generally lower than those in the United States and other Western countries. This cost advantage can significantly reduce operational expenses, especially in labor-intensive industries. As wage and transportation inflation rises in other countries like China, Mexico’s cost-effectiveness has become even more attractive for manufacturers.
- Strong Manufacturing Infrastructure: Mexico has developed a robust manufacturing infrastructure, including industrial parks, specialized zones, and modern facilities. This infrastructure supports various industries, from automotive and aerospace to electronics and medical devices. The growth of shelter corporations and programs like IMMEX (formerly the Maquiladora Program) also allows for duty-free importation of raw materials, further streamlining operations.
- Free Trade Agreements: Mexico has an extensive network of free trade agreements, including the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which provides favorable trade conditions. These agreements facilitate the import and export of goods and materials, reducing trade barriers and costs for businesses. Preferential tariffs and efficient logistics networks enable companies to move goods with little to no tariffs, making cross-border trade smoother.
- Specialized Clusters: Mexico has established industry clusters in specific regions, such as the automotive cluster in the Bajío region and the aerospace cluster in Querétaro. These clusters offer access to specialized suppliers, knowledge sharing, and a highly skilled workforce. Gone are the days of only simple assembly and low-tech manufacturing in Mexico. Today, the country attracts major multinational manufacturers across virtually every sector. For example, Tijuana in Baja California boasts the largest concentration of medical device manufacturers in all of North America, making it a recognized leader in this field. Additionally, Mexico has become the fourth largest producer of automobiles in the world, reflecting the country’s significant evolution and expertise in advanced manufacturing. These specialized clusters not only support industry growth but also foster innovation and collaboration, further strengthening Mexico’s status as a premier outsourcing destination.
- Regulatory Environment: Mexico has tried to create a more business-friendly regulatory environment, including streamlining permitting processes and improving intellectual property protection. This encourages foreign investment and outsourcing activities. While some regulations have been streamlined to ease business setup, companies also benefit from established programs supporting manufacturing operations.
- Language and Cultural Affinity: Mexico's proximity to the United States means that many Mexicans are bilingual, making communication with English-speaking clients and partners more accessible. Cultural affinity also facilitates business relationships and understanding.
- Scalability: Mexico offers scalability options for businesses of all sizes. Whether it's setting up a small operation or a large-scale manufacturing facility, companies can find suitable solutions to meet their production needs. The country’s growing and diversified workforce allows businesses to easily expand production as demand increases.
- Quality Standards: Mexico is committed to high-quality production standards. Businesses can benefit from the country's focus on quality control and adherence to international quality management systems. Gone are the days of only simple assembly and low-tech manufacturing—Mexico now attracts large, multinational manufacturers from virtually every industry, emphasizing advanced production and innovation.
- Lower Overhead Costs: Mexico's relatively low overhead costs, such as rent, utilities, and administrative expenses, contribute to outsourcing cost-effectiveness.
- Access to a Growing Consumer Market: Beyond its role as an outsourcing destination, Mexico also serves as a growing consumer market. This dual advantage allows businesses to produce and sell products in the region.
- Growth in Consumer and Electronics Manufacturing: Many consumer products companies have shifted their manufacturing operations to Mexico to leverage these advantages. The electronics manufacturing sector, in particular, is experiencing significant growth, as global demand for consumer electronics rises and more companies tap into Mexico's engineering and design talent. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the U.S. Consumer goods market remains the largest in the world, underscoring the strategic importance of proximity to this market for manufacturers based in Mexico.
Overall, Mexico’s manufacturing sector has evolved far beyond basic assembly, now encompassing advanced industries and offering significant advantages for companies seeking efficiency, quality, and market access. With a combination of skilled labor, competitive costs, extensive infrastructure, and favorable trade agreements, Mexico stands out as a top choice for manufacturing outsourcing.
Leveraging the IMMEX Program for Consumer Product Manufacturing
An additional advantage for consumer product manufacturers in Mexico is access to the IMMEX Program (formerly known as the Maquiladora Program). This government initiative enables companies to import raw materials and components duty-free, provided that the finished goods are later exported.
For manufacturers, this translates to significant cost savings on materials and more streamlined operations. By removing tariffs on imported inputs, the IMMEX Program enhances Mexico’s appeal as a production site—especially for companies focused on efficiency and global market reach. This favorable framework makes it easier for businesses to establish local shelter corporations, optimize supply chains, and accelerate time-to-market for consumer goods.
Impact of USMCA on Mexico’s Automotive Industry
The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) has introduced new requirements that directly influence automotive manufacturing and export dynamics in Mexico. Under the USMCA, at least 75% of a vehicle’s content must originate from North America—specifically, from Mexico, Canada, or the United States. This represents a significant increase compared to the previous North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) threshold.
For manufacturers in Mexico, these rules of origin drive greater demand for locally sourced auto parts, incentivizing investment and expanding opportunities for domestic suppliers. Not only does this spur job creation within the country, but it also strengthens integration across the North American supply chain.
Alongside the local content stipulations, automakers are encouraged to source critical components—such as engines, transmissions, and key assemblies—from regional partners. By aligning supply and production to meet these new regulations, Mexican facilities enhance their appeal as vital links for both exporters and assemblers in the U.S. and Canada. These adjustments collectively support long-term growth, boost workforce development, and create a more competitive and resilient manufacturing base across the continent.
Challenges in Mexican Manufacturing
While Mexico's manufacturing processes offer numerous advantages, they also come with their share of challenges.
Common Challenges
- Security Concerns: Certain regions of Mexico face security issues, including drug-related violence and crime. This can threaten business operations and employee safety.
- Regulatory Complexity: Mexico's regulatory environment can be complex and bureaucratic, requiring careful navigation to ensure compliance with local laws and regulations. This includes labor laws, environmental regulations, and customs procedures.
- Labor Relations: While Mexico has a skilled workforce, labor relations can sometimes be challenging. Issues related to unions, labor disputes, and worker demands affect operational stability.
- Infrastructure Gaps: While Mexico has made significant investments in infrastructure, there are gaps in transportation, utilities, and telecommunications, particularly in rural areas.
- Language and Cultural Differences: Communication challenges can arise due to language differences and cultural nuances, especially for non-Spanish-speaking companies.
- Political Uncertainty: Political changes and policy shifts in Mexico or its trade partners, such as the United States, can impact trade relations and regulations.
- Environmental Concerns: Increased scrutiny of environmental sustainability and compliance can lead to additional costs and regulatory challenges for manufacturers.
- Logistics and Transportation Costs: While Mexico's proximity to North American markets is an advantage, transportation costs, especially on long-distance routes, can be a challenge. Logistics and transportation solutions are crucial.
- Talent Retention: Competition for skilled labor can make talent retention and recruitment challenging, particularly in specialized industries.
- Currency Exchange Risks: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact manufacturing costs in Mexico for companies operating in different currencies.
- Customs and Trade Compliance: Ensuring proper customs documentation and trade compliance can be complex, especially for businesses that import raw materials and export finished products.
Conclusion
Mexico's manufacturing processes have evolved significantly, reflecting a dynamic and resilient industry. From embracing automation and sustainability to navigating challenges and shaping future trends, Mexico continues to be a powerhouse in the world of manufacturing. As we look ahead, it's clear that Mexico's manufacturing sector is poised for further growth and innovation.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are the key industries driving manufacturing processes in Mexico?
- Mexico's key manufacturing industries include automotive, electronics, aerospace, and more, each contributing significantly to its manufacturing landscape.
2. How is automation impacting manufacturing in Mexico?
- Automation and robotics are enhancing efficiency, precision, and productivity in Mexican manufacturing processes, resulting in cost savings and improved quality control.
3. What is lean manufacturing, and how is it applied in Mexico?
- Lean manufacturing is a philosophy that focuses on efficiency and waste reduction. In Mexico, it is implemented to optimize operations and improve competitiveness.
4. What role does sustainability play in Mexican manufacturing?
- Sustainability is a priority in Mexican manufacturing, with eco-friendly practices, renewable energy adoption, and waste reduction initiatives contributing to a greener industry.
5. What are the future trends in Mexican manufacturing?
- The future of Mexican manufacturing is expected to include advanced technologies, increased sustainability efforts, and continued growth in key industries such as automotive and electronics.
About NovaLink
As a manufacturer in Mexico, NovaLink employs a unique approach that transcends the traditional model of shelter production. More than just the location of your manufacturing, we would like to become a partner in your manufacturing in Mexico. You will be able to relocate or initiate manufacturing for your company in Mexico in a low-cost labor environment with very little delay or up-front costs. Find out how we can help you by handling the manufacturing process.
There are NovaLink facilities in the border cities of Brownsville, Texas, Matamoros, Mexico, and Saltillo, Mexico.
Explore More: Discover Related Blog Posts
Expand your knowledge and delve deeper into Mexico Industrial Manufacturing with our curated collection of related blog posts.
- Why “Plan Mexico” Might Be the Wake-Up Call Manufacturers Didn’t Know They Needed
- Why Factories in Mexico Are the Preferred Choice for Nearshoring
- 5 Easy Steps to Move Your Production to a Mexican Factory
- 3 Key Benefits of Operating in Mexico’s Border Zone
- Shaping the Future: Innovations in Sustainable Manufacturing in Mexico